Franchises are a fundamental part of the American business landscape, spanning a diverse range of industries and sectors. From popular fast-food chains like McDonald’s and Subway to hotel brands like Marriott and Hilton, franchises are deeply woven into daily life. While these and other household names like 7-Eleven, Dunkin’, and The UPS Store are well-known franchise brands, many people may be surprised to learn that even indoor pickleball courts, escape rooms, cryotherapy centers, and pet grooming services often operate under franchise models. These businesses not only cater to a wide range of consumer interests but also create pathways for entrepreneurs to own and operate their own firms.
In recent years, franchise businesses have also become increasingly important drivers of job growth and economic output, currently representing around 9% of all U.S. business establishments and nearly 6% of total employment. According to the International Franchise Association (IFA), franchise business growth is expected to outpace the broader U.S. economy in the coming year, fueled by stronger consumer demand, improving labor supply, and advancements in automation software and AI. By 2025, franchise economic output is projected to exceed $936 billion, with employment in the sector surpassing 9 million workers.
Using newly released data from the IFA and the Projections Managing Partnership, this analysis by Cinch—a franchise marketing software company—examines the role of franchise businesses in state-level job growth. By comparing franchise-specific employment projections to those of the broader labor market, this report highlights how franchises are shaping the availability of jobs across the country.
Here are some of the key findings from the study:
- Franchise employment is growing faster than the national average. Franchise jobs are projected to grow 4.7% between 2023 and 2025, outpacing the 2.4% overall employment growth rate. Franchises will account for 5.8% of total jobs and 11% of total job growth, adding 402,000 positions and surpassing 9 million workers.
- Quick-service restaurants (QSR) lead in franchise employment, but personal services are growing fastest. QSR franchises will employ over 4 million workers in 2025, while personal service franchises (e.g., fitness centers, salons, childcare) will see the fastest growth at 7.8%.
- The Southeast has the highest franchise employment share. Nine of the top 10 states with the largest proportion of total jobs in franchise businesses are in the Southeast, with South Carolina (8.8%), Georgia (7.1%), and Louisiana (6.7%) leading. Lower costs and fewer employment regulations drive this trend.
- In four states, franchises drive more than half of all job growth. South Carolina (87.5%), Maine (73.4%), Idaho (57.2%), and Louisiana (53.9%) rely heavily on franchise expansion for new job creation.
- Franchise job growth is slowing in high-cost states. Several states, including California, New York, and Illinois, are seeing franchise employment decline, even as overall job numbers rise.
Industries That Employ the Most Franchise Workers
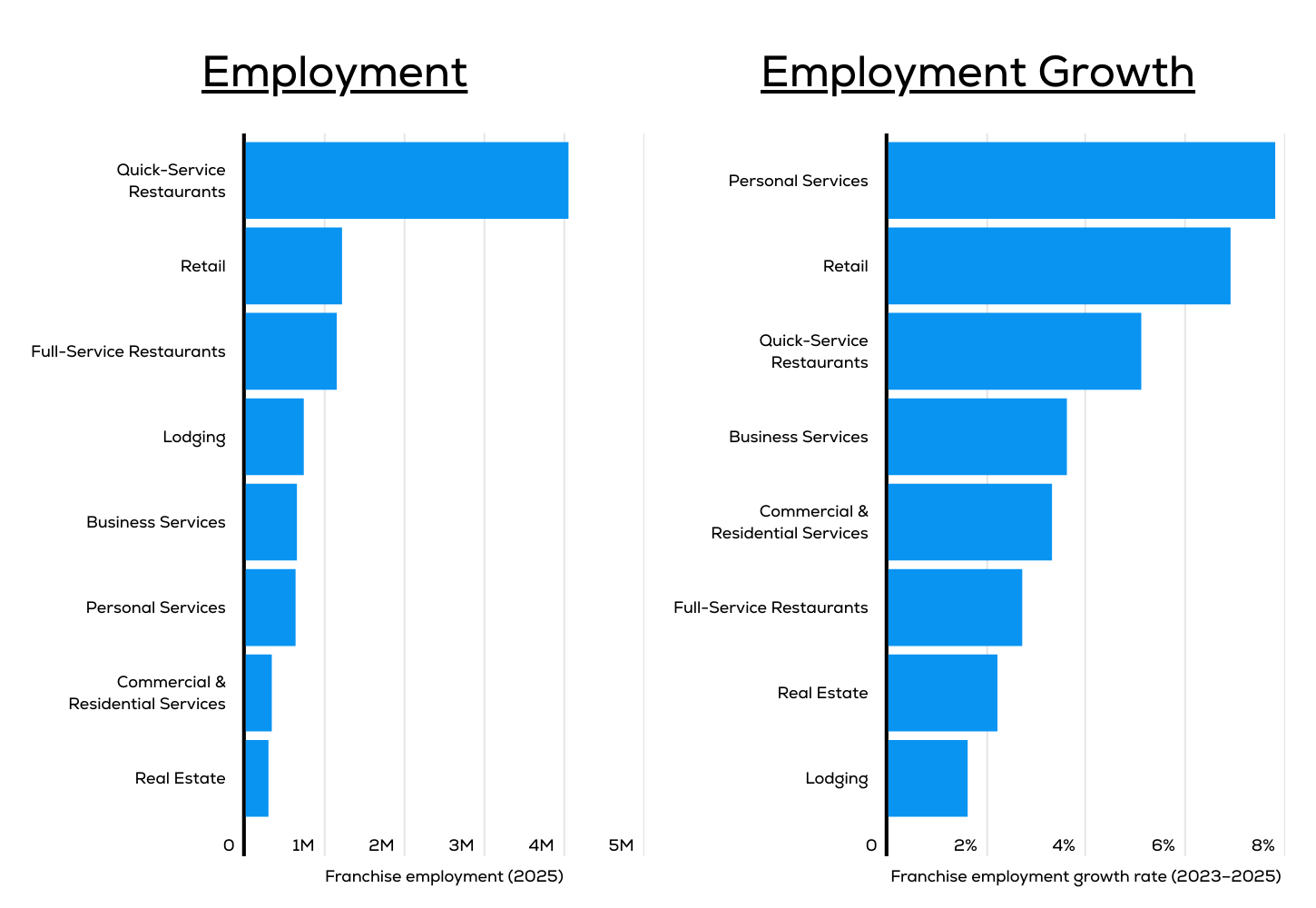
Source: Cinch analysis of FRANdata statistics
Franchise employment is heavily concentrated in quick-service restaurants (QSRs), which are by far the largest source of franchise jobs in the U.S. In 2025, QSR franchises are projected to employ more than 4 million workers, making up a significant portion of the overall franchise workforce. Other major employers in the franchise sector include retail (1.2 million workers), full-service restaurants (1.1 million workers), and lodging (728,000 workers). These industries rely on the franchise model to expand their reach, benefiting from brand recognition and standardized operations to maintain consistency across locations.
While QSRs dominate in total employment, the fastest-growing segment is personal services, which includes businesses such as fitness centers, beauty salons, childcare services, and health & wellness providers, among others. Employment in personal services franchises is projected to grow by 7.8% between 2023 and 2025, outpacing all other sectors. The retail sector follows closely behind, with franchise employment expected to increase by 6.9% over the same period. Despite their already large workforce, QSR franchises continue to expand, with employment projected to increase by 5.1% by 2025.
The Top States for Franchise Employment
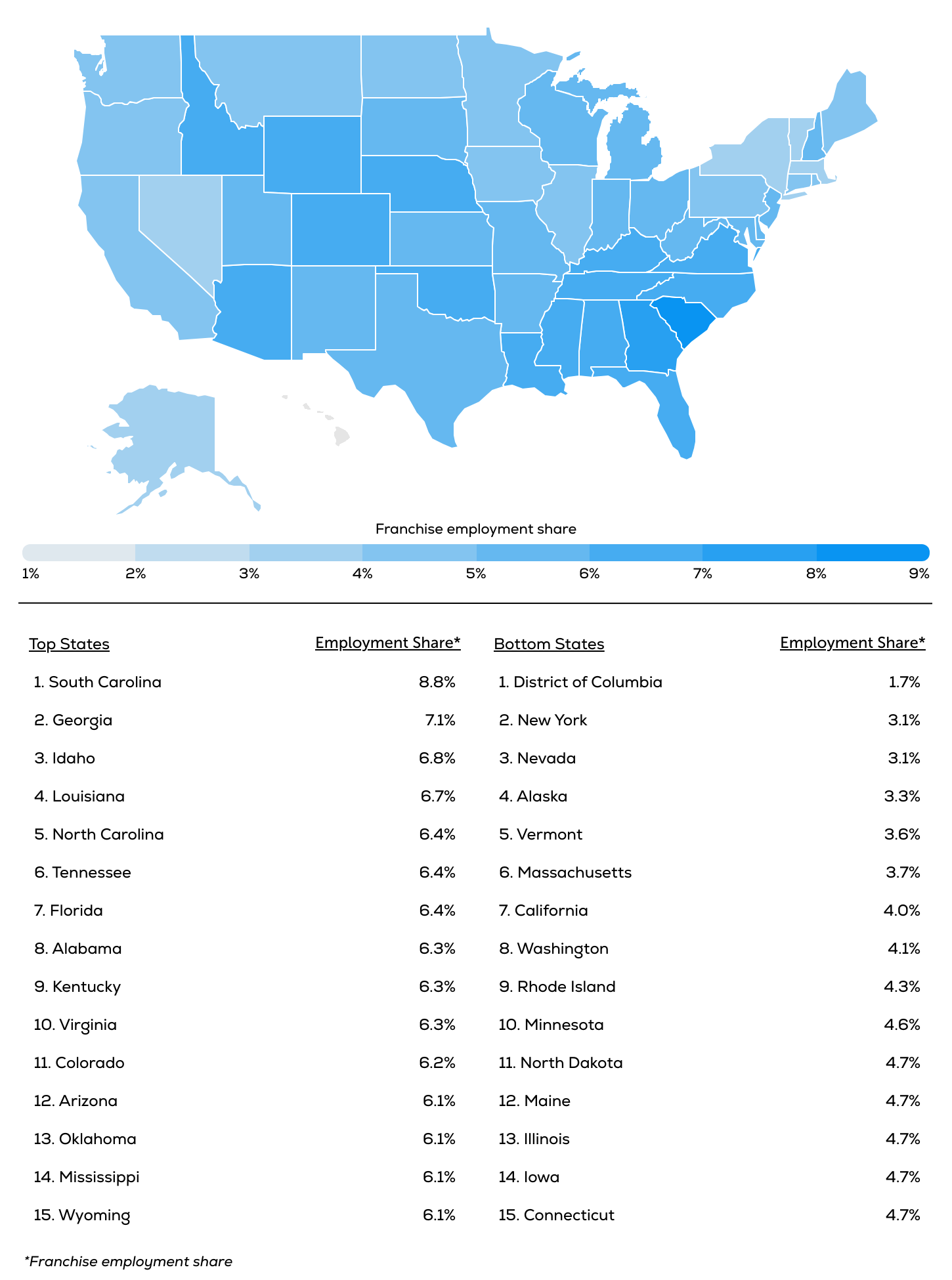
Source: Cinch analysis of FRANdata and Projections Managing Partnership statistics
Franchise employment is particularly strong in the Southeastern U.S., which accounts for nine of the top 10 states with the largest share of franchise workers. In South Carolina, 8.8% of the workforce is projected to be employed by franchises in 2025, the highest in the country and well above the national average of 5.8%. Other states with high franchise employment shares include Georgia (7.1%), Idaho (6.8%), and Louisiana (6.7%). Several other Southern states—including North Carolina, Tennessee, Florida, and Alabama—also rank among the top ten, underscoring the region’s strong reliance on franchise businesses for jobs.
The Southeast’s strong franchise presence can be attributed to several factors, including lower taxes, reduced operating costs, and fewer labor regulations. Additionally, many of these states have seen an influx of new residents in recent years, driving demand for food service, retail, and personal service franchises.
Conversely, franchise employment is least concentrated in the Northeast and on the West Coast. The District of Columbia is projected to have the lowest share of franchise employment this year (1.7%), followed by New York and Nevada (both 3.1%). Other states with lower franchise employment shares include Massachusetts (3.7%), California (4.0%), and Washington (4.1%). In these regions, higher labor costs and stricter regulations may limit franchise expansion compared to other parts of the country.
Where Franchises Are Driving the Most Job Growth
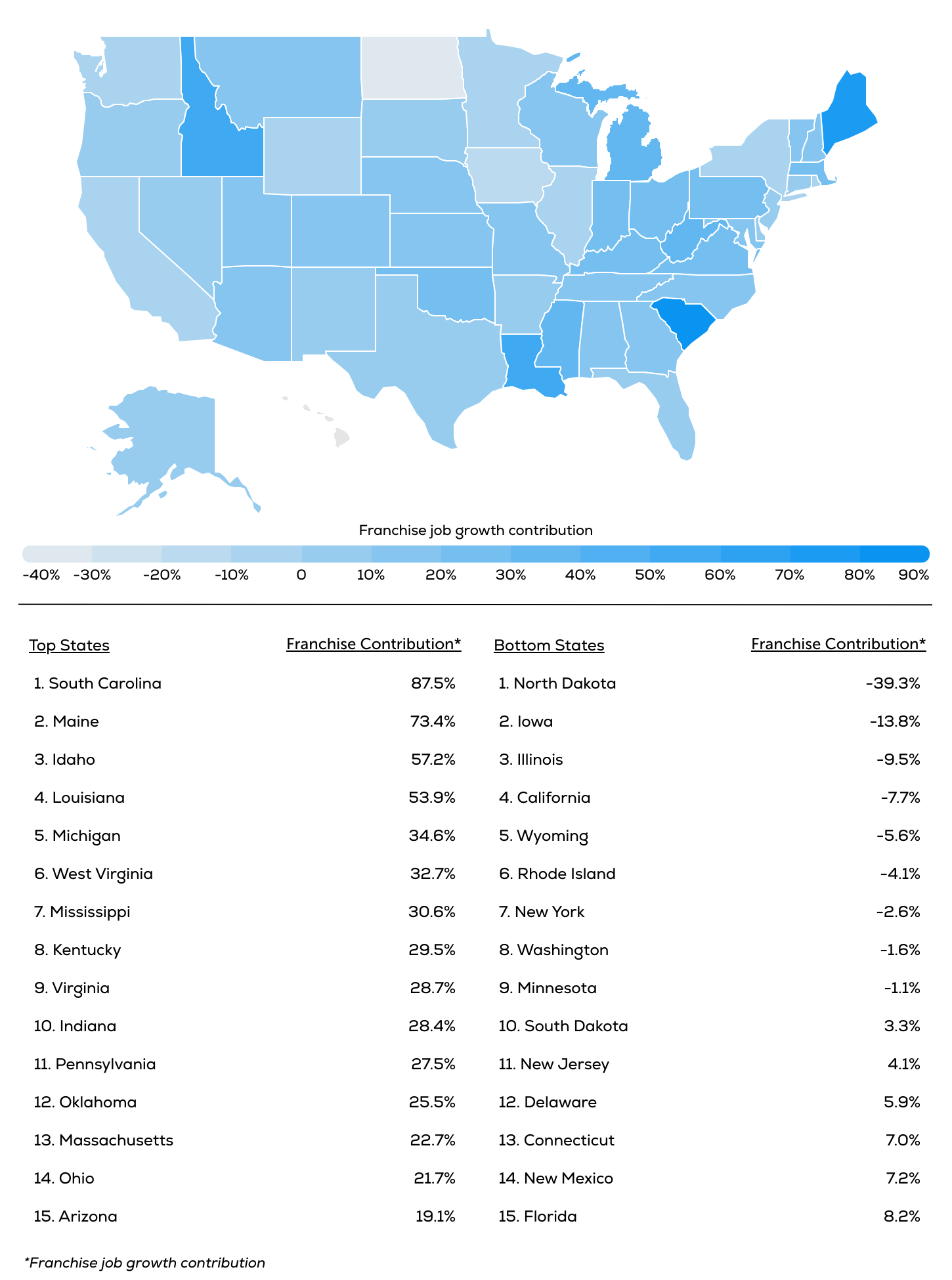
Source: Cinch analysis of FRANdata and Projections Managing Partnership statistics
While franchise businesses are projected to account for 11% of total U.S. job growth between 2023 and 2025, some states will rely on the growing franchise sector more heavily than others.
South Carolina leads the nation, where franchise jobs are expected to drive nearly 88% of total employment growth. Between 2023 and 2025, franchise employment in the state is set to grow by 27.9%, adding 47,018 new jobs, while total employment will increase by just 2.3%. Similarly, Maine’s franchise sector is set to expand by 22.6%, accounting for 73.4% of the state’s total job growth, despite overall employment increasing by just 1.2%. Idaho (57.2%) and Louisiana (53.9%) also stand out, with more than half of new jobs coming from franchises.
By contrast, franchise employment is shrinking in high-cost states like California, New York, and Illinois, even as total job numbers rise. California’s total employment is expected to grow by 2.5%, but franchise employment is projected to decline by 4.5%. This trend highlights how higher operating costs and stricter regulations may be limiting franchise expansion in these markets.
Overall, the Southeast remains a hotspot for franchise job growth, while the West, Northeast, and parts of the Midwest are seeing slower or negative franchise employment trends. These patterns reflect the role of state-level economic conditions and business policies in shaping the future of franchising and employment growth across the U.S.
For a detailed state-by-state breakdown of franchise and total employment projections, see the original version on Cinch: How Franchise Businesses Are Driving Job Growth in Each State.
Methodology

Photo Credit: Maderla / Shutterstock
To assess the impact of franchise businesses on job growth at the state level, researchers at Cinch analyzed employment trends between 2023 and 2025. The study focused on the extent to which franchise employment growth contributes to overall job growth in each state. The key metrics used in this analysis include:
- Franchise job growth contribution: The percentage of total employment growth in a state that is attributed to franchises.
- Franchise employment share: The proportion of total workers in each state employed by franchise businesses.
- Franchise employment growth: The absolute and percentage change in the number of franchise employees from 2023 to 2025.
- Total employment growth: The absolute and percentage change in overall state employment (non-farm wage and salary workers) during the same period.
The total employment figures for 2023 and projected employment numbers for 2025 were sourced from the Projections Managing Partnership’s Short-Term Occupational Projections (2023–2025), a widely used dataset for labor market forecasts. Franchise employment statistics for 2023 and projections for 2025 were derived from the 2025 Franchising Economic Outlook Report, a joint project by the International Franchise Association (IFA) and FRANdata, which examines trends in franchising across the U.S. Due to a lack of data availability from the Projections Managing Partnership dataset, Hawaii was not included in the study.
For complete results, see How Franchise Businesses Are Driving Job Growth in Each State on Cinch.